Objects of Highway Pavement design :
- The surface of the roadway should be stable and non-yielding
- The objective of laying pavements is to support wheel load and transfer the load stresses through wider area
It is always desirable to construct the pavements well above the maximum level of the ground water or the highest water table.
Requirements of Highway Pavements :
Road vehicle able to travel at the design speed without undue discomfort . There are two major requirements –
a) Functional Requirements – road user point of view (good riding quality,less slippery,do not deform surface under wheel load)
b)Structural Requirements- highway engineering point of view(sustain the heavy wheel load and their repeated applications,various design factor related to drainage -climate-environmental)
Types of Pavement Structure :
Based on structural behaviour it is two categories-
a)Flexible pavement
b)Rigid Pavement
Others types of pavements structure include Semi-rigid /composite pavement Pavement,Interlocking Concrete Block Pavement (ICBP)
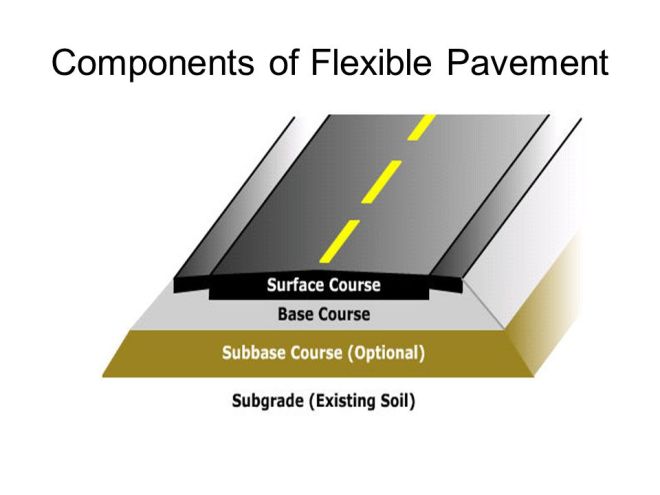
a) Flexible Pavement :
- Low flexural strength and flexible
- The vertical compressive stress is maximum on the pavement surface , this is decreased at the lower layers.
- Transfer of load here ‘ grain to grain’ for this reason ‘pavement layer system concept’ was develop.
- The top layer to be strongest as the highest compressive stress are to be sustain by this layer in addition to wear and tear.
b) Rigid Pavement :
- High Flexural Strength
- Rigid Pavement generally made of ‘Portand cement concrete’ with or without steel reinforcement at the joint.
- It’s expected to sustain up to 45kg/cm2 of flexural strength
- Rigid pavement has the ‘slab action ‘ and is capable of transmitting the wheel load stresses through a much a wider area below the pavement slab.
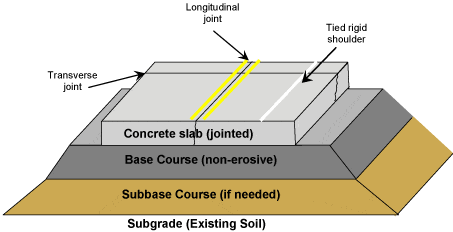
Rigid Pavement
Others Types of Pavements :
i) Semi -rigid and composite Pavements:
- Pozzolanic concrete ( lime-flyash-aggregates) or soil cement are used in the sub-base course of the pavement layer.
- Some chemical are form semi rigid layer
- low resistance to impact and abrasion and therfore not used in surface course.
ii) Interlocking cement concrete Block Pavement (ICBP)
- Consist of a layer of cement concrete paver block
- The gap between the paver block are filled with joint filling sand and vibrated so as to provide adequate interlocking between the blocks.
It’s used when pavement is to be constructed in water-logged area or get submerged under water.
Comparison of Flexible and Rigid Pavement :
i) Design Life- a) Design life of flexible pavement is 15 years.
b) Design life of Rigid Pavement is 30 Years.
ii) Curing Period – a) For Flexible it is 24 hours .
b) For Rigid it is 28 days.
iii)Total Thickness – a) Total thickness is higher than Rigid Pavement.
b) Total thickness is less than the Flexible Pavement.
iv)Life Cycle Cost – a) Life cycle cost (Include initial,maintenance,
strengthening)are higher than the Rigid Pavement.
b) Life cycle cost is low.
v) Night Visibility – a) very poor for flexible pavement.
b)Good Night Visibility even under wet condition.
Your explanations are going to help students a lot. Great work…..
LikeLike
Thanks for your valuable feedback!
LikeLike